Audio engineering is a broad field, and there’s a lot more to it than you might think. With a wide range of career options and responsibilities, audio experts can perform a myriad of jobs. Here is your ultimate guide to what audio engineering is, so you can understand the ins and outs of the audio world.
What Does an Audio Engineer Do?
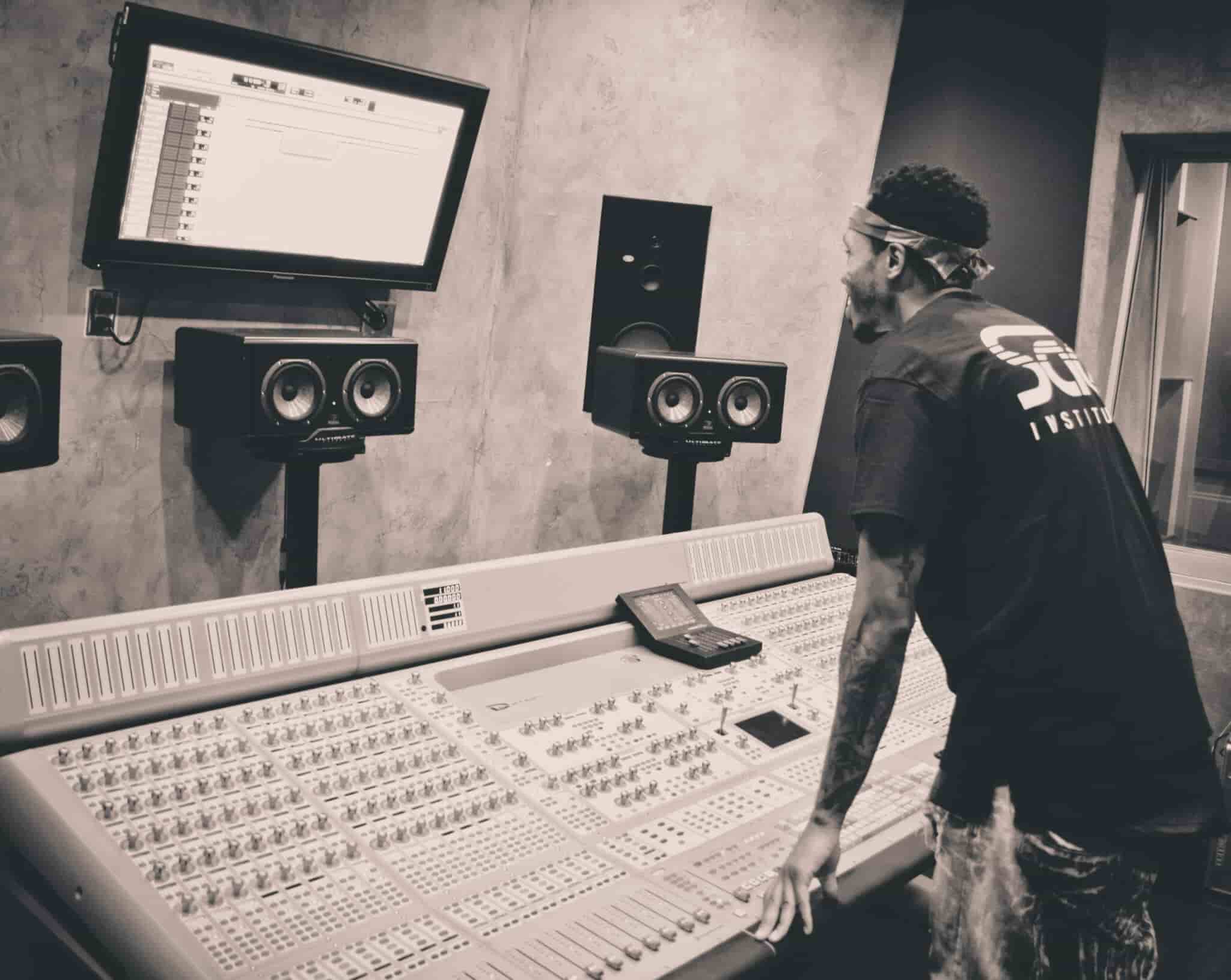
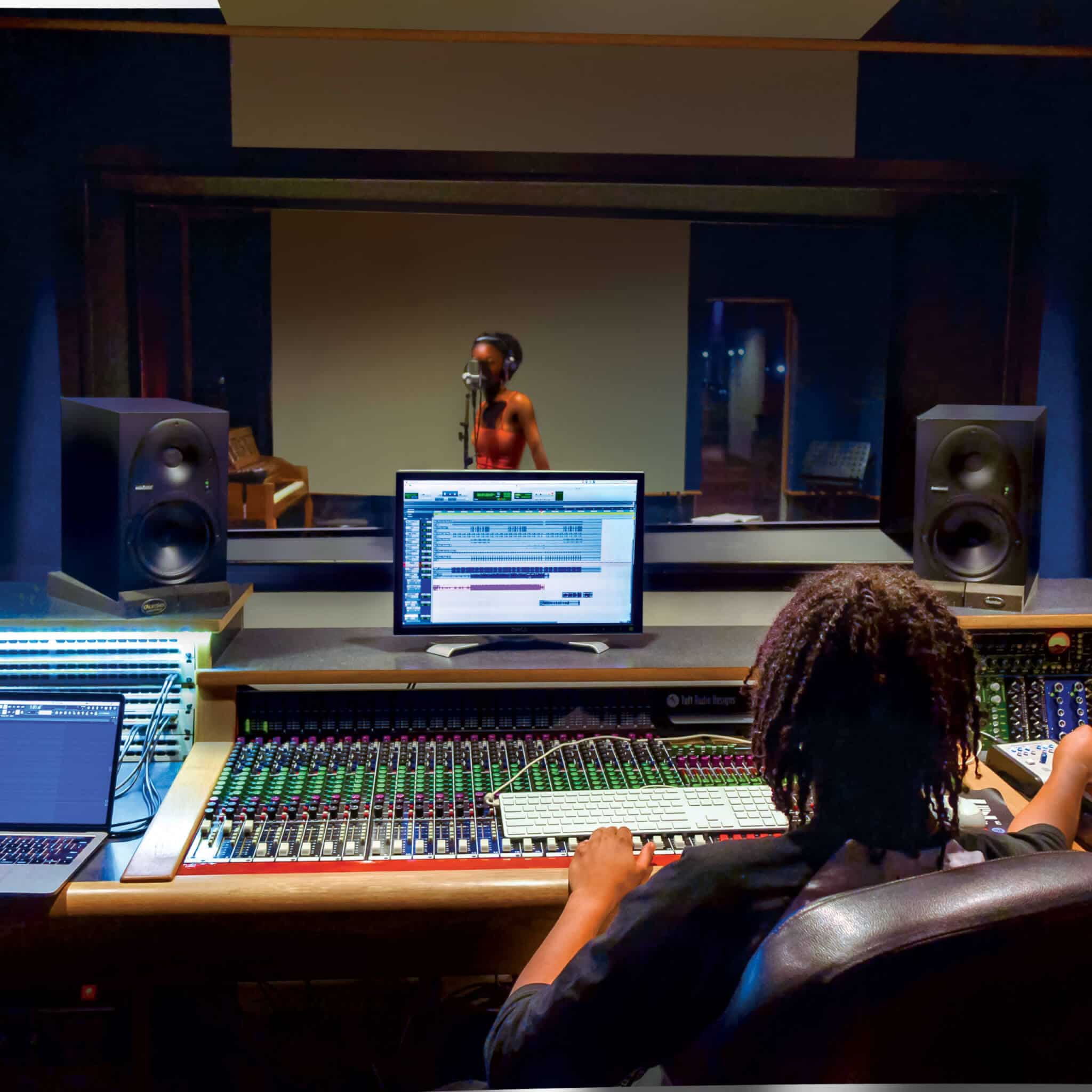
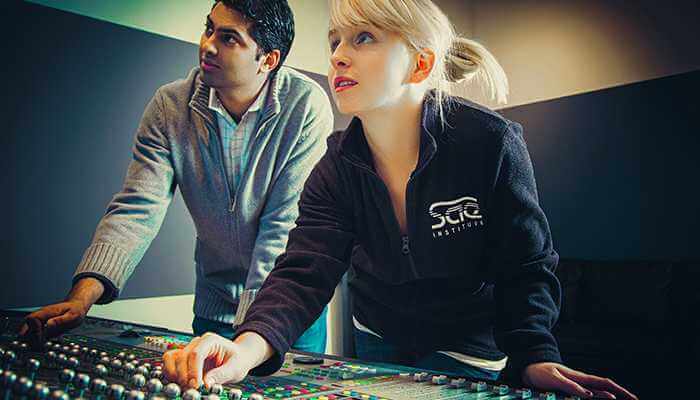
An audio engineer (also known as a sound engineer) works with all of the mechanics of recording, mixing, and reproducing sound. Audio engineers aren’t the performers or producers of music or audio—they are the experts who deal with the technical and mechanical aspects of sound.
When you think about a recording studio, the audio engineer is the person sitting behind the large board of knobs and sliders. It is their job to regulate the various volume levels and to ensure the best sound quality.
What Are Career Paths for an Audio Degree?
There’s so much more to audio production and management than just audio engineering. With an audio degree, you open the doors to work in a wide variety of careers.
Here are just a few of the careers you can pursue with an audio degree.
Live Audio Engineer
A live audio engineer (sometimes called Live Sound Engineer) steps out of the production room and into music venues. They use their training and knowledge to help live performances sound their best and to record live productions. Some live audio engineers even join musicians on tour, making sure that each stop has the right sound quality.
Audio Broadcast Engineer
Also known as broadcast and sound engineers or broadcast technicians, these experts maintain the electrical equipment for radio programs, television broadcasts, concerts, or other media programs. Where other audio experts specialize in the recording and production of audio, broadcast engineers focus primarily on live broadcasts.
Game and Audio Design Engineer
The sounds of video games are sometimes more famous than the game they go with. Game and audio design engineers focus on not just the background music but the sound effects and noises heard throughout a game.
Audio Production Assistant
Production assistant (PA) refers to a broad category of jobs. While PAs can do just about anything, their main role is to act as the intermediary between everyone involved in a project. They get all parties ready for the production, communicate instructions or directions, and ensure that everything is ready to go. The PA is often the first one in and the last one out of a recording session.
Mastering Engineer
Depending on the size and structure of the recording studio, there can be complex nuances between the different roles of the engineers that work there. You might see different positions like tracking engineers, mixing engineers, and mastering engineers. In many companies, however, especially in smaller production companies, those roles are covered entirely by the mastering engineer. A mastering engineer is responsible for polishing and refining a recording to make it sound as great as possible. It’s their job to remove tonal imbalances, white noise, or any other mistake or blemish that shows up in the recording.
Music Producer
While an audio engineer is faced with the technical side of audio recording, a producer tackles creative and managerial tasks. Producers work alongside musicians, performers, and audio engineers to help reach a production goal or vision. A producer will help choose songs, write or suggest changes to the piece, and even coach artists throughout their recordings. They work to achieve a specific sound they have in mind and to bring out the best of the artists.
Post-Production Expert
You might have heard someone say before that they’re unhappy with what they’ve created, but they’ll “fix it in post.” Post-production experts are the ones responsible for all of those fixes. Projects typically go into post-production for the final refinement and polishing of the piece. Post-production includes recording and synching voiceover, audio FX, foley, and ADR for film or TV. Each of these ensures that the audio in the completed product is high quality.
Sound Designer
A sound designer works in both film and live theatre; they are the artistic director in charge of the audio experience, using audio to help create and enhance the mood, atmosphere, and tone of a scene. This helps create an immersive experience for the audience because both the visuals and audio need to work together to help transport the audience.
How Do You Become an Audio Engineer?
If you want to become an audio engineer, there are a couple of different paths you can take. Here’s what you need to know about your options so you can determine which path is right for you.
Self-Taught
It is possible to learn how to become an audio engineer without any formal training or education. The benefit of taking this route is you don’t have to worry about paying for school or taking time away from your current career. One downfall to learning how to become a professional audio engineer without any formal training is it might lead to a lot of failures or simple mistakes and errors that could have been avoided. The other disadvantage of being self-taught is that some companies will prioritize people with a degree until you have a large portfolio to showcase projects you have worked on.
Higher Education
There are a variety of training or degree programs that can help you gain the knowledge and training you need to learn audio engineering. These programs are built with your future in mind and aim to help you be prepared for the career of your dreams. An audio degree or diploma can give you an extra edge over your competition when applying for a job opening. Degrees also help you start to build your portfolio through various projects and assignments you work on throughout your program.
Audio Programs at SAE Institute
At SAE Institute, our audio programs include four different paths you can take. You can earn an audio diploma or an audio technology diploma in as little as twelve months, earn your Audio Associate of Applied Science in as little as 16 months, or earn your Audio Bachelor of Applied Science in 32 months.
With each program at SAE Institute, you will learn and develop skills that will help you in your future career like:
- Recording and mixing
- Audio engineering
- Music programming
- Live performance engineering
- Electronic music production
- Video game audio creation and integration
- Post-production
- Adaptive audio integration
No matter which program you enroll in, we offer a curriculum that helps our students become prepared both technically and creatively. Our industry-standard equipment will help you build your knowledge and skills to help you gain practical training, as well as guided development in a series of projects specially developed to demonstrate knowledge to prospective employers.
Refine Your Portfolio
A large part of being an audio engineer isn’t just what you know, but seeing that knowledge in practice. Whether you entered through a degree program or you’re self-taught, your next goal should be to continually improve your portfolio. Your portfolio should showcase your best jobs, any specialties you have, as well as a diverse showcase of genres and styles of jobs you have worked on. If you’re looking to be competitive for more popular or high-end jobs, you have to have a portfolio that showcases your skills.
Prepare for Your Future at SAE Institute
At SAE Institute, you know you’re getting a quality education from an accredited institution that can prepare you for your future. Contact us today about our audio programs to find out more about what audio engineering is and how we can help you reach your goals.